Securing Drupal: Storing API Tokens in Lockr
As seen in the recent Uber hack, storing secrets such as API tokens in your project repository can leave your organisation vulnerable to data breaches and extortion. This tutorial demonstrates a simple and effective way to mitigate this kind of threat by leveraging Key module to store API tokens in remote key storage.
Even tech giants like Uber are bitten by poor secret management in their applications. The snippet below describes how storing AWS keys in their repository resulted in a data breach, affecting 57 million customers and drivers.
Here’s how the hack went down: Two attackers accessed a private GitHub coding site used by Uber software engineers and then used login credentials they obtained there to access data stored on an Amazon Web Services account that handled computing tasks for the company. From there, the hackers discovered an archive of rider and driver information. Later, they emailed Uber asking for money, according to the company.
Uber could have avoided this breach by storing their API keys in a secret management system. In this tutorial, I'll show you how to do exactly this using the Key module in conjunction with the Lockr key management service.
This guide leverages a brand-new feature of Key module (as of 8.x-1.5) which allows overriding any configuration value with a secret. In this instance we will set up the MailChimp module using the this secure config override capability.
Service Set-Up
Before proceeding with the Drupal config, you will need a few accounts:
These third-party services provide us with a simple example. Other services are available.
Dependencies
There are a few modules you'll need to add to your codebase.
composer require \ "drupal/key:^1.5" \ "drupal/lockr" \ "drupal/mailchimp"
Configuration
- Go to /admin/modules and enable the MailChimp, Lockr and Key modules.
- Go to /admin/config/system/lockr
- Use this form to generate a TLS certificate that Lockr uses to authenticate your site. Fill out the form and submit.
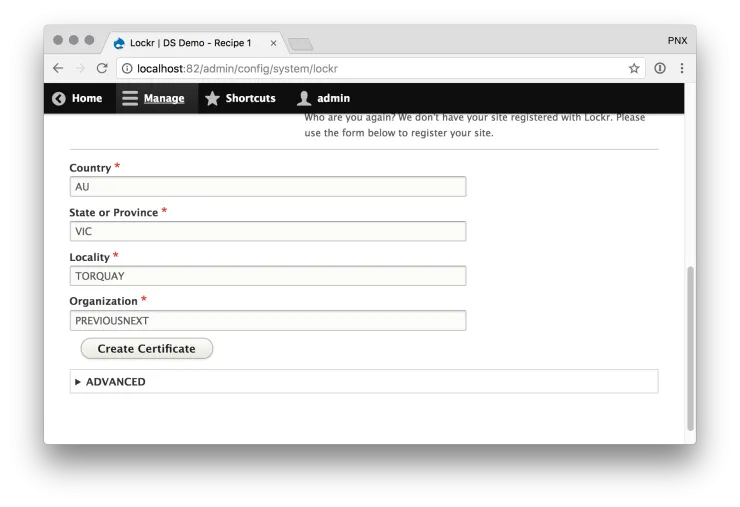
- Enter the email address you used for your Lockr account and click Sign up.
- You should be now be re-prompted to log in - enter the email address and password for your Lockr account.
- In another tab, log into the MailChimp dashboard
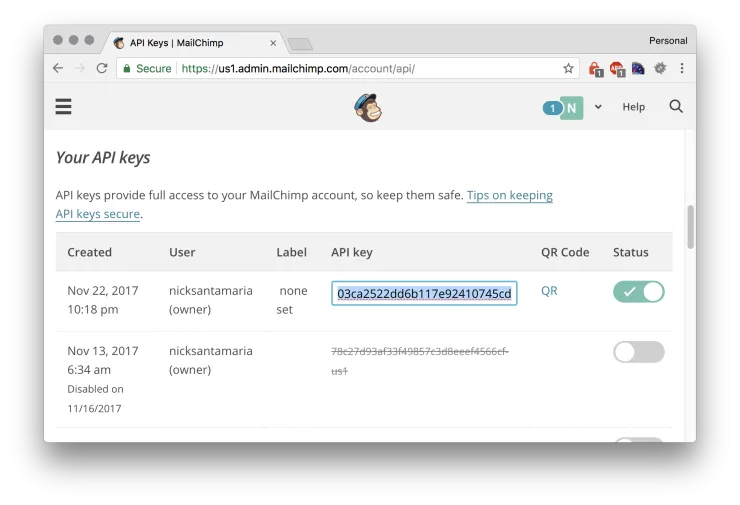
- Go to the API settings page - https://us1.admin.mailchimp.com/account/api/
- Click Create A Key
- Note down this API key so we can configure in Drupal in the next step.
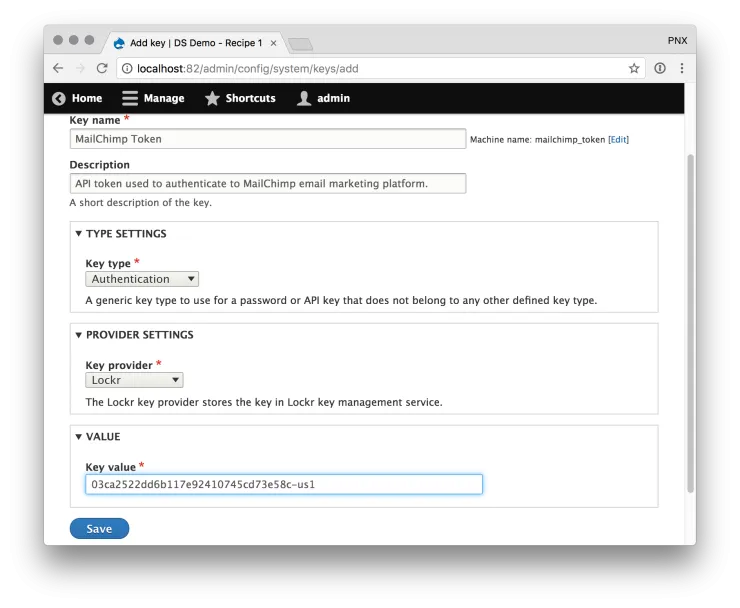
- In your Drupal tab, go to /admin/config/system/keys and click Add Key
- Create a new Key entity for your MailChimp token. The important values here are:
- Key provider - ensure you select Lockr
- Value - paste the API token you obtained from the MailChimp dashboard.
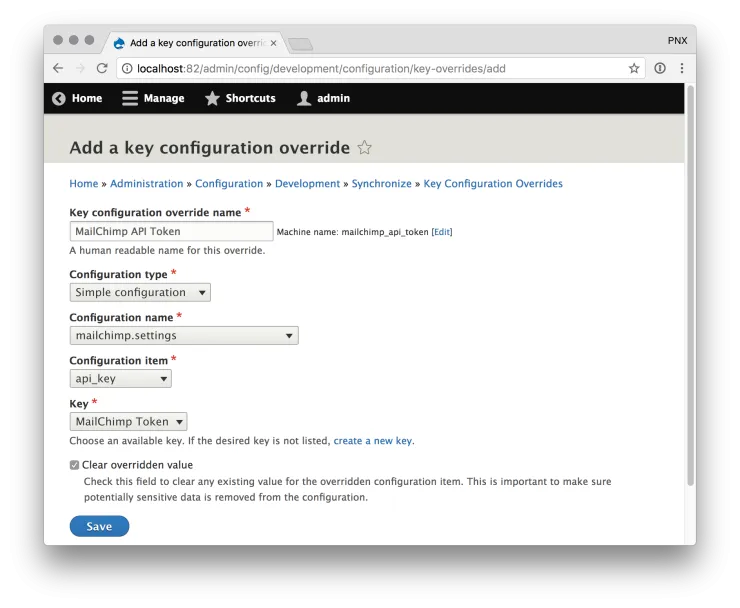
- Now we need to set up the configuration overrides. Go to /admin/config/development/configuration/key-overrides and click Add Override
- Fill out this form, the important values here are:
- Configuration type: Simple configuration
- Configuration name: mailchimp.settings
- Configuration item: api_key
- Key: The name of the key you created in the previous step.
... and it is that simple.
Result
The purpose of this exercise is to ensure the API token for our external services are not saved in Drupal's database or code repository - so lets see what those look like now.
MailChimp Config Export - Before
If you configured MailChimp in the standard way, you'd see a config export similar to this. As you can see, the api_key value is in plaintext - anyone with access to your codebase would have full access to your MailChimp account.
api_key: 03ca2522dd6b117e92410745cd73e58c-us1 cron: false batch_limit: 100 api_classname: Mailchimp\Mailchimp test_mode: false
MailChimp Config Export - After
With the key overrides feature enabled, the api_key value in this file is now null.
api_key: null cron: false batch_limit: 100 api_classname: Mailchimp\Mailchimp test_mode: false
There are a few other relevant config export files - lets take a look at those.
Key Entity Export
This export is responsible for telling Drupal where Key module stored the API token. If you look at the key_provider and key_provider_settings values, you'll see that it is pointing to a value stored in Lockr. Still no API token in sight!
dependencies: module: - lockr - mailchimp id: mailchimp_token label: 'MailChimp Token' description: 'API token used to authenticate to MailChimp email marketing platform.' key_provider: lockr key_provider_settings: encoded: aes-128-ctr-sha256$nHlAw2BcTCHVTGQ01kDe9psWgItkrZ55qY4xV36BbGo=$+xgMdEzk6lsDy21h9j…. key_input: text_field
Key Override Export
The final config export is where the Key entity is mapped to override MailChimp's configuration item.
status: true dependencies: config: - key.key.mailchimp_token - mailchimp.settings id: mailchimp_api_token label: 'MailChimp API Token' config_type: system.simple config_name: mailchimp.settings config_item: api_key key_id: mailchimp_token
Conclusion
Hopefully this tutorial shows you how accessible these security-hardening techniques have become.
With this solution implemented, an attacker can not take control of your MailChimp account simply by gaining access to your repository or a database dump. Also remember that this exact technique can be applied to any module which uses the Configuration API to store API tokens.
Why? Here are a few examples of ways popular Drupal modules could harm your organisation if their configs were exposed (tell me about your own worst-case scenarios in the comments!).
- s3fs - An attacker could leak or delete all of the data stored in your bucket. They could also ramp up your AWS bill by storing or transferring terabytes of data.
- SMTP - An attacker could use your own SMTP server against you to send customers phishing emails from a legitimate email address. They could also leak any emails the compromised account has access to.
What other Drupal modules could be made more securing in this way? Post your ideas in the comments!
Go forth, and build secure Drupal projects!